Table of Contents
Togglegingivitis vs periodontal disease : What's the difference?
gingivitis vs periodontal disease , Maintaining good oral health is essential for overall well-being. Two common dental issues that people often encounter are gingivitis and periodontal disease. Understanding the differences between these conditions can help you take better care of your oral health.
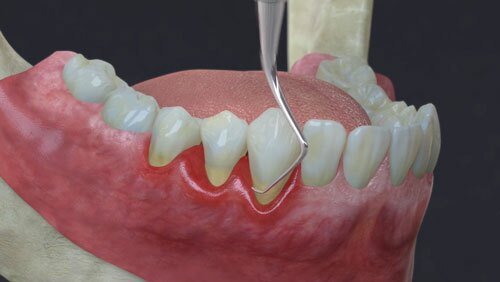
Gingivitis: The Mild Starter
gingivitis vs periodontal disease , often referred to as gum inflammation, is a mild and common form of gum disease. It usually results from poor dental hygiene, where plaque and bacteria accumulate on the teeth and gums. Some key characteristics of gingivitis include :
Bleeding Gums: Gingivitis often manifests as bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing.
Redness and Swelling: The gums may appear red and swollen.
Bad Breath: Foul-smelling breath, or halitosis, can be a sign of gingivitis.
No Bone or Tissue Damage: At this stage, gingivitis affects only the gum tissue and doesn’t cause bone loss.
Fortunately, gingivitis is reversible with improved oral hygiene practices and regular dental check-ups.
What is gingivitis, and how can it be treated?
Gingivitis is a mild form of gum disease characterized by inflamed gums. It can often be treated with improved oral hygiene practices, regular dental check-ups, and professional cleanings at a clinic like Kristal Clinic.
How does gingivitis differ from periodontal disease?
Gingivitis is a less severe form of gum disease that only affects the gum tissue. Periodontal disease, in contrast, is an advanced stage with potential bone loss and tooth mobility, requiring professional care and sometimes surgical treatments provided by specialists like those at Kristal Clinic.
What are the common symptoms of periodontal disease, and when should I seek professional help?
Symptoms of periodontal disease include gum recession, tooth mobility, and pus formation. If you notice these signs, it's crucial to consult a dental specialist. Kristal Clinic offers expertise in the treatment and management of periodontal disease.
How can I prevent both gingivitis and periodontal disease?
Prevention involves regular dental check-ups at a trusted clinic, like Kristal Clinic, practicing good oral hygiene, a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco.
Why should I choose Kristal Clinic for my gum health concerns?
Kristal Clinic is a reputable dental clinic known for its expertise in treating various gum conditions, including gingivitis and periodontal disease. Their experienced team can provide you with personalized care and treatment options tailored to your specific needs.
Periodontal Disease: The Advanced Stage
Periodontal disease, on the other hand, is a more severe form of gum disease. It develops when gingivitis is left untreated, and it can lead to more serious oral health issues. Some features of periodontal disease include:
Gum Recession: The gums may start to recede, creating pockets between the teeth and gums.
Bone Loss: Periodontal disease can lead to bone loss, which can affect the stability of teeth.
Tooth Mobility: As the condition progresses, teeth can become loose or shift in position.
Pus Formation: Pus may develop in the pockets between the teeth and gums.
Periodontal disease requires professional treatment, which may include scaling and root planing, antibiotics, and, in severe cases, surgery. It’s essential to address periodontal disease promptly to prevent further damage.
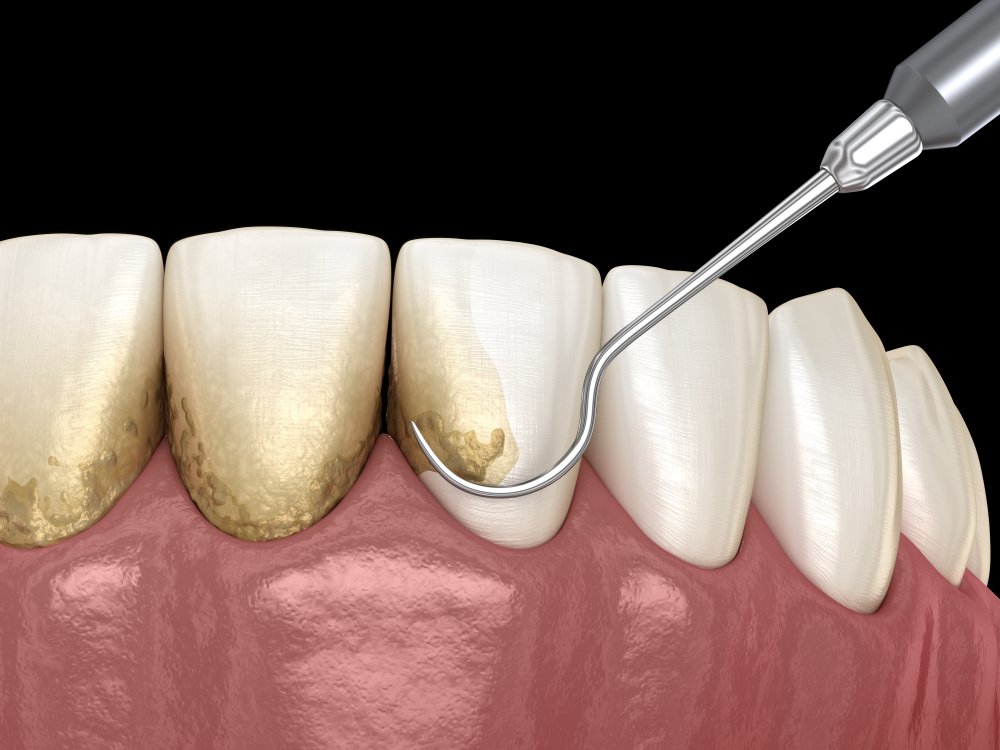
Prevention and Treatment
To maintain good oral health and prevent both gingivitis and periodontal disease, follow these practices:
Regular Brushing and Flossing: Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles.
Dental Check-ups: Visit your dentist for regular check-ups and professional cleanings.
Healthy Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support oral health.
Avoid Tobacco: Smoking and chewing tobacco can contribute to gum disease.
In conclusion, gingivitis and periodontal disease represent different stages of gum disease, with gingivitis being the milder form and periodontal disease being more advanced and potentially serious. By maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking professional care when needed, you can prevent and manage these conditions effectively.
If you have concerns about gum disease and require dental care, it’s advisable to contact a trusted dental clinic like Kristal Clinic for expert guidance and suitable treatment options. For specific promotional content and clinic information, it’s best to reach out to them directly.